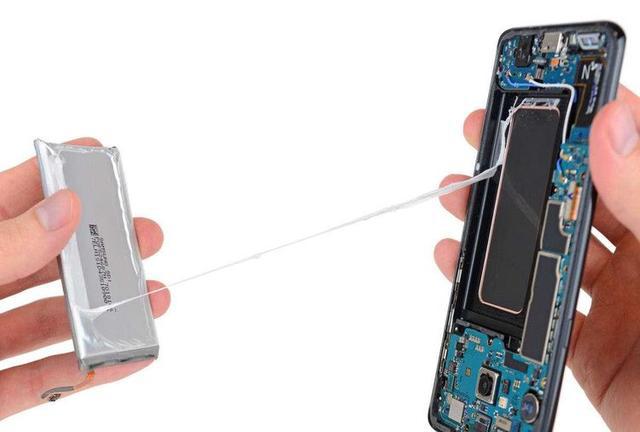
Does that mean mobile phones with replaceable batteries will become the mainstream design in the future?
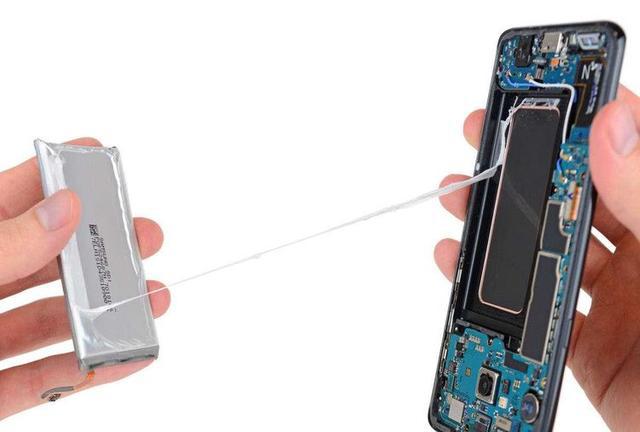

First, mobile phones are unlikely to be designed as thin and light as they are today.
Let’s first take a look at the disadvantages of the removable battery.
Second, after changing to a removable battery, some charging functions may have to be cancelled.
In today’s mobile phones with non-removable batteries, the outer skin of the lithium battery inside is made of aluminum-plastic film. You can think of it as the outer shell of the battery, but it is very thin, with a thickness of only 0.1mm, which is not a shell.
Regardless of the thinness, it is also divided into three layers-a nylon layer, which provides ductility; an aluminum layer, which provides structural protection and can also prevent the electrolyte in the battery from evaporating; and a PP layer, which is made between the aluminum layer and the electrolyte insulation. Because it is wrapped, a total of only 0.2mm thickness is added to the base of the battery. The installation of the battery does not require an additional frame structure, as long as the aluminum-plastic film is fixed with double-sided tape.
And if you switch to a removable battery, the phone’s battery will be much thicker. First of all, in order to comply with the safety standards of various countries, the previous form of the soft case is no longer possible. Instead, a hard case needs to be set outside the battery. The thickness of the case is about 1mm, and the two sides add up to 2mm.
Because the battery is hard-packed and the volume is fixed, it is necessary to set a vent valve in accordance with the explosion-proof design requirements of the lithium battery, and leave a certain amount of space for the swelling of the battery, which will waste about 1mm of thickness.
In addition, because the battery can be taken out by hand, a separate battery compartment must be provided between the battery and the motherboard to prevent the motherboard from being directly touched by the hand. This battery compartment should be at least 1mm thick.
In order for the battery to be removable, there is more space that needs to be set aside. After the detachable design is adopted, the safety test items of the mobile phone will also be adjusted. In order to pass the impact damage experiment, the battery must be separable from the phone body when violently beaten. This is also the reason why mobile phones from a long time ago sometimes fell to the ground, and the casing, battery, and body were scattered all over the place. This is actually an indication that the mobile phone meets the standard. In order to achieve this, it is necessary to have a certain margin in the battery installation slot, which cannot be stuck tightly, so a certain amount of thickness is wasted.
Therefore, to achieve the same capacity, removable batteries are at least 5mm thicker than non-removable batteries. But as long as you look up the new phones released in the last 3 years, you will find that few phones have a total thickness of more than 9mm. Just to replace the battery with a removable one, the thickness will be more than 50%, which is a bit expensive.
Third, there is no hand feeling and the design is ugly.
For example, the hottest fast charge at the beginning was only 40W, and later competed to 55W and 65W. Today, 120W fast charge has appeared. Calculate, the voltage on the positive and negative poles of the battery is about 4V, and charging with 120W power is about 30A. For a battery as small as a mobile phone, this pressure is extremely high.
In the past, removable batteries were charged by spring contacts against the batteries. This is not a problem at low currents, but at a current of 30A, that little contact area will not work at all, and it will soon lead to local high temperatures due to excessive contact resistance. High temperature is the most important factor leading to battery life loss or damage.
To handle such a large current, the correct method is to use a nickel tape, which is a strip of metallic nickel, which can ensure a larger area of contact. There will be no high contact resistance when the current is too large, and it will not cause local high temperature.
Of course, this difficulty is not impossible to solve, such as using multiple batteries in parallel, or designing a set of contact methods when charging, and it can be separated from the discharged set. However, the space required for these designs can be far more than an increase of 5mm in thickness, and it is unlikely that merchants will do this for fast charging. Moreover, the feature of detachable battery itself replaces fast charging to a large extent, so canceling the fast charging function seems to be a more reasonable choice.
There is also a very practical function, which is estimated to be cancelled, which is wireless charging. Because in the case that the thickness of the mobile phone has increased a lot, a wireless charging coil and related circuit have to be added on the back, which is too crowded and the possibility of cancellation is also high.
Fourth, mobile phones with removable batteries have to compromise on waterproofing and heat dissipation.
In addition, many of the exquisite hand feel of today’s mobile phones are derived from the shells made of precision-processed metal, glass, and ceramics. Once replaced with a removable battery, because it must meet the standard of “the battery can be separated from the body during violent testing” in the safety test, it must be easy to disassemble the back case, so the phone back case can only be made of engineering plastics. Although in theory glass and metal back shells are also possible, the cost will be much higher, and it may not look good. The only real choice is engineering plastics. Therefore, this will cause the phone to feel completely lost.
Many mobile phones now support bare-metal waterproofing. For example, Apple’s iPhone 11 Pro and Samsung’s Galaxy S20 both support IP68 waterproof. At least it’s okay to soak for a few minutes under 1 meter underwater. Once the battery is detachable, the back cover can be broken off by hand, the waterproof effect will disappear immediately, and the dust proof effect will be greatly reduced.
If waterproofing is still required, only additional sealing strips and sealing plugs can be designed, just like the three-proof mobile phones 10 years ago. In this way, in order to waterproof function, but also to thicken a few millimeters.
Take a step back and say that even if the sealing strip is used for waterproofing, because it isolates the flow of heat, the heat dissipation of the mobile phone will be poor. In addition, even if it is not waterproof, just because a battery compartment is added to the removable battery, the chip on the mobile phone motherboard will change from the original one shell to two layers, and the heat dissipation will not be as good as before, and some top chips may not be able to. It is used in this type of mobile phone, or can only be used after a significant frequency reduction.
The above four points are the disadvantages of mobile phones with removable batteries. Of course, it is not that these four points cannot be overcome at all, but that if they are to be overcome, each of them needs extra thickness to achieve. Maybe a mobile phone with the same battery capacity as today, but after changing from a non-removable battery to a removable battery, the thickness will increase by more than 1cm. The total thickness of the mobile phone is 1.8cm, which is the same thickness as today’s two mobile phones stacked together, and the weight has doubled. I think this is something that many people cannot accept.